Long gone are the days of spamming links in comment sections on WordPress to manipulate search algorithms. In the modern SEO landscape, content is king, keyword intent matters, and traffic doesn’t mean much without conversion optimization.
While SEO has often gotten a bad rap over the years, quality and ethics are more important than ever before.
While many of these bad SEO practices focus on Google-centric metrics, remember that AI-powered platforms like ChatGPT or Perplexity also factor in content quality, credibility, and user satisfaction.
A misguided tactic—like keyword stuffing or purchasing backlinks—could ruin your standing in these emerging channels, limiting your reach as more people turn to AI search for answers. Future-proofing your content means aligning with best practices that uphold trust, whether it’s on Google or the next big AI-driven platform.
Whether your website is suffering as a result of manipulative tactics or by sheer accident, we have outlined eleven bad SEO practices that you need to avoid.
The Importance of Ethics in SEO
In many people’s minds, ethical SEO is an oxymoron like organic link-building or creative advertising.
However, many of the bad SEO practices or shortcuts people have practiced over the years do not work anymore.
That’s why Google’s evolving focus on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is not just about checking boxes—it’s about cultivating lasting user trust. If your content showcases genuine expertise, helpful real-life experiences, and transparent motives, it’s far more likely to satisfy both search engine algorithms and human visitors.
By prioritizing E-E-A-T principles, you avoid bad SEO practices and simultaneously future-proof your brand reputation across all search platforms.
Even the top results for any cooking recipe on Google have over one thousand words and provide evergreen information to help you follow along.
Therefore, ethical SEO is not just a moral question; it’s a practical one. We can outline a million best practices to follow, but if your marketing team is lazy or you hire a company that is unethical, your results will suffer.
Still, we believe marketing agencies have an obligation to help their clients as best as they can, just as any doctor or professional should. Just because agencies are built to make money doesn’t mean they should put money over the interests of their clients. Again, it’s just not practical.
With that said, if you are unsure how an agency is treating you or worried about your current campaign results, the culprit may just be one of these eleven bad SEO practices.
1. Promising Overnight Results
Here’s a tactic that most unethical SEOs use before they even click into your analytics. Let this be your biggest agency red flag. SEO results cannot happen overnight. While some situations can have positive results quickly, the real benefits take a few months.
John Mueller of Google previously stated that it could take weeks just for new content to be crawled and indexed.
From this point, it can take months of consistent, high-quality content to establish trust, build links organically, and generate traffic.
Solution: Set realistic expectations. Let clients or superiors know that SEO may be a long game, but the results will pay for themselves (and then some) if done properly.
2. Keyword Stuffing
Implementing keywords in your content is vital for results. However, when done in excess, it can have negative consequences in search.
Google lists keyword stuffing as one of its spam policies that can result in a penalty for your website.
Don’t start stuffing in keywords on every blank space of your site just to manipulate rankings.
Solution: Implement keywords naturally. Often, we encourage our writers to write an article as naturally as possible. Then, if the opportunity exists, we will go in after and populate the text with a few strategic keywords where it makes sense.
3. Paid Links
When done correctly, link-building can yield very positive results. When done incorrectly, it can damage your site’s reputation and be difficult to recover from.
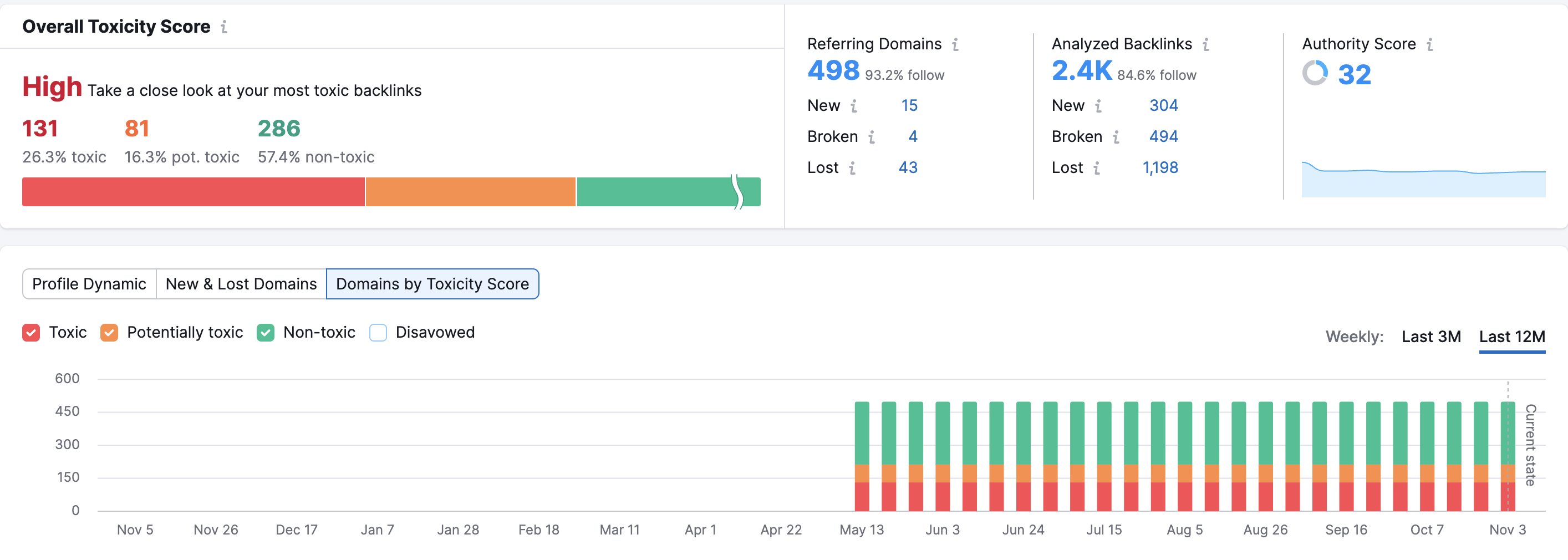
Be sure to conduct a link audit of your existing backlink profile using a tool like SEMrush.
By reviewing the links individually, you can actually see where a majority of spam links arise from. In some cases, they may be done inadvertently without your knowledge.
With that said, you still have the responsibility to disavow these links and show Google you are not buying links directly to avoid a penalty against your rankings.
Solution: Collect a list of all URLs that you suspect are paid–use a tool to determine this–and upload them to Google’s Disavow tool.
4. Cloaking
Cloaking presents readers with misleading information to trick them into visiting a website. An example of this would be an internal link and anchor text for “wedding dresses” that takes you to a webpage about truck tires.
While cloaking is considered a spammy practice, most search engines are smart enough to pick up on it, so it’s fairly useless.
Solution: Ensure consistency across your site. Ensure all links have relevant anchor text to the page they are linking to.
 5. Duplicate Content
5. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is often completed inadvertently through pagination, AMP pages, or just sheer dumb luck. However, duplicate content will result in a penalty for that piece of content and is generally considered a bad SEO practice.
Solution: Implement canonical tags on the original page you want to be indexed and insert a 301 redirect on duplicate pages you don’t want indexed.
6. Clickbait
Like cloaking, clickbait is a shock and awe tactic used to draw users in using cleverly worded titles. These “hot-button” titles are filled with misleading lead-ins that attempt to get clicks and boost rankings.
Now, this isn’t to say that catchy headlines are spammy. But, if you have a headline titled, “Google Reveals this Tactic Will Get Your Website to #1,” and Google does not reveal anything, then this would be considered very spammy.
Solution: Create a headline-writing formula for catchy blog titles that don’t deceive people.
7. Writing for the Search Engines
Content marketers should always write for humans first and robots second.
Search engines are only successful when customers are happy. So, if you start pumping out spammy, keyword-stuffed content that is impossible to read, search engines will shy away from those pages.
Solution: Focus on LSI keywords. Make content read more naturally by implementing a little keyword diversity. Instead of spamming target keywords into every paragraph, experiment with supplemental keywords in headers and other paragraphs. This will provide users with a broader range of information and help answer more questions along the way–meaning more traffic opportunities.
8. Focusing Too Much on Domain Authority
Domain Authority (DA) is a somewhat useful algorithm created by Moz to score domains on a number of best practices. Google does not use DA as a ranking factor, nor does it serve as any correlation to your likelihood to rank for any particular keyword. Beware of companies that try to sell DA management as a service or as an important KPI for its reporting.
Solutions: Use better analytics. Look at user behavior in SERPs (Google Search Console) and once they land on your website (Google Analytics) to optimize pages for the highest engagement and conversion rate. There are a number of free content analysis tools that will help you better optimize your website to follow SEO best practices.
9. Spinning Content
Spinning content has long been considered a bad SEO practice, but it has only gotten worse in the age of AI.
While the question of whether Google can detect AI content or even if it’s deemed harmful is nuanced, best practices generally recommend that the content you do create “adds value.”
AI-generated content can be a game-changer when used ethically—think research support or drafting outlines. But the line between “assisted writing” and “mass-produced fluff” is thin. While spinning content is a textbook bad SEO practice, blindly churning out AI-driven articles without human oversight can be just as detrimental.
Always ensure every piece of AI-influenced writing undergoes thorough editing, fact-checking, and contextual tailoring. This not only protects your brand from duplicate or low-quality output but also keeps your content valuable and personalized.
Solution: Don’t use AI to generate massive amounts of spam content. Instead, use AI like ChatGPT to optimize your workflow by performing valuable tasks, such as research, which enable you to write more content.
10. Spamming Anchor Text
Optimizing anchor text is a best SEO practice, but you should not sacrifice the quality of your content to fit in some strategic keywords where it doesn’t make sense.
Spamming the same keyword phrase into every bit of anchor text will be noticed by search engines and viewed with suspicion.
Solution: Apply LSI keywords to different forms of anchor text and use internal linking strategically to bolster the most bang for your buck.
11. Writing Poor Content
Every red flag on this list leads to bad content, and in turn, you won’t get the results you want out of your SEO campaign. If the goal of SEO is to build more traffic to your website, then you need quality content to do so.
Solution: Avoid all of these bad SEO practices we listed above and try to write evergreen content that answers as many user questions as possible. Performing advanced keyword research and SERP analysis will help you reach these results.
As new AI search engines gain traction, best practices will continue to evolve. Techniques deemed acceptable today may be frowned upon tomorrow.
By committing to real user value, transparent intent, and continuous improvement, you’ll remain resilient amid algorithm updates—whether they come from Google or the latest AI-powered competitor. In the end, the common denominator for any successful SEO strategy will always be authentic, user-centric content.
FAQs: Bad SEO Practices
How can I identify if my website is engaging in bad SEO practices?
A precipitous drop in keyword rankings could be a sign that your website is in violation of some Google penalty or algorithm update. Otherwise, if you are not getting the desired results from an SEO campaign, you will need to perform a technical audit of all existing site features and content to identify any bad SEO practices.
What are the consequences of bad SEO practices on website rankings?
Bad or spammy SEO practices can result in a significant drop in keyword rankings or the inability to get new content to rank highly for a specific keyword.
How can I recover from the penalties imposed by search engines due to bad SEO practices?
First, identify the source of the problem. Some common bad SEO practices include paid links, keyword stuffing, cloaking, and duplicate content. Next, fix these problems and resubmit your sitemap to Google to reindex your web pages and eliminate any existing search engine penalties. This process could take months to properly rectify.