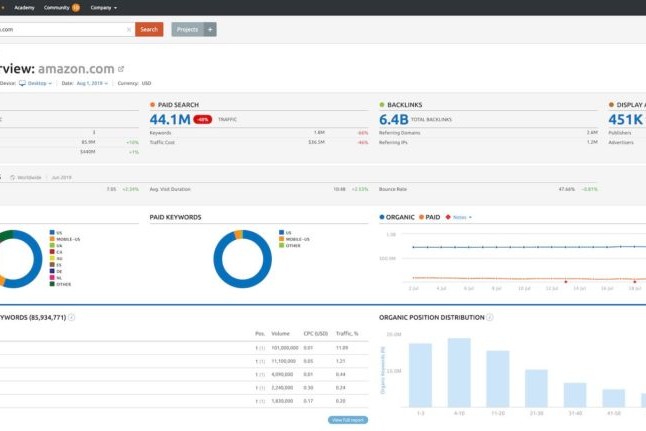
The rise of applications like ChatGPT promise to streamline many tedious applications for companies to help them save money and grow.
On the other hand, the rise of generative AI has also produced some uneasiness among people of every industry as the sophistication of AI becomes more clear to everyday viewers.
A recent AI-generated movie trailer for a parody of The Great Gatsby, called The Great Catsby shows how visually advanced generative AI has become a creative force in our society.
We’ve used AI for several years, whether it’s your everyday content analysis tool or advanced keyword research. But now AI has grown to the point that it can write its own blogs and create its own images.
In this blog, we’ll explore the role of generative AI for marketers and how to responsibly leverage generative AI to assist your workflow.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that uses algorithms to create new content or solutions by learning from past data. It falls under the broad category of machine learning and can generate an answer to almost any question it’s asked, making it increasingly popular in various industries.
Broader applications of generative AI incorporate unsupervised neural networks, which allow AI algorithms to learn from their own amongst an endless number of variables and patterns.
While generative AI remains in its infancy, its rate of scale and the number of different applications coming to market will mean that this technology is advancing faster than we can control it.
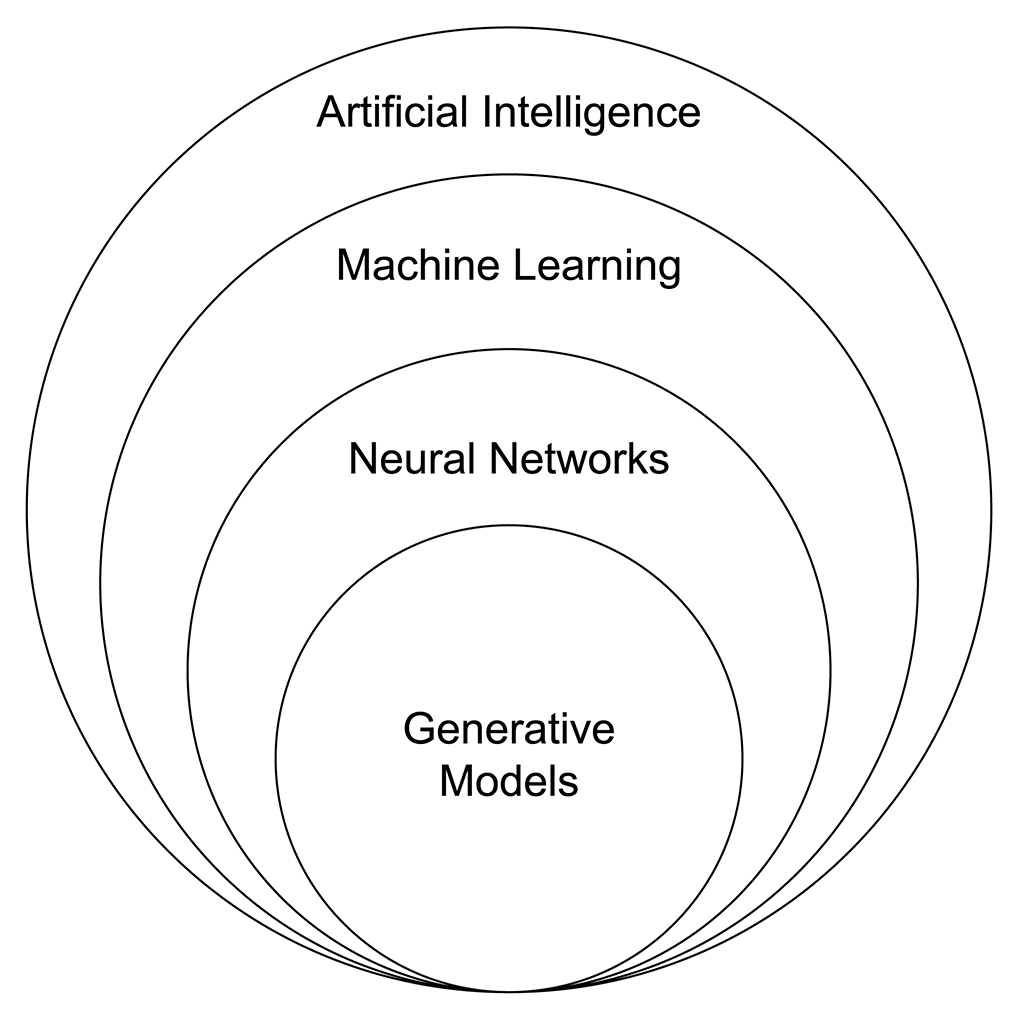 Key Differences Between Generative AI and Other Forms of AI
Key Differences Between Generative AI and Other Forms of AI
So what makes generative AI better or scarier than traditional forms of AI and machine learning?
Traditional AI models rely on pre-established regulations or classified datasets to generate results. In contrast, generative AI utilizes huge amounts of unstructured data without explicit direction to collect patterns and create entirely novel outputs.
While traditional AI models, such as rule-based systems or supervised machine learning techniques, rely on predefined rules or labeled datasets for generating output, generative AI learns patterns from vast amounts of unstructured data without explicit guidance. This enables them to produce entirely new content based on their understanding.
Some key characteristics of generative AI include:
- Generating Text: Tools like OpenAI’s GPT-3 are capable of creating authentic-sounding text passages by identifying patterns within massive volumes of textual data.
- Create Specialized Models: With Google’s BERT model, SEO campaign managers can fine-tune pre-trained language models for specific tasks such as sentiment analysis or document classification.
- Innovate with Images: Dall-E 2 is another example where researchers have used generative AI tools to create unique images based on input descriptions.
The Role Of Large Language Models (LLMs) In Generative AI
Large language models (LLMs) play a crucial role in the development and success of generative AI. These colossal neural networks are taught on extensive amounts of text data, permitting them to comprehend grammar, syntax, semantics, and even some facts about the universe.
LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-3 have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating coherent and contextually relevant text across a wide variety of domains.
Their ability to adapt to different tasks without extensive retraining has made LLMs increasingly popular for content creation purposes.
In fact, they can be fine-tuned for specific industries or applications by exposing them to more targeted datasets during training. This enables businesses to leverage these powerful models to produce high-quality content tailored to individual user preferences.
Applications of Generative AI in Business
Businesses are leveraging generative AI for various applications such as generating computer program code, translating code, managing text-based knowledge within organizations across different industries, and helping shoppers decide on products based on their preferences and requirements.
As a result, generative AI models have the potential to profoundly transform how businesses operate and engage with customers.
Nestle uses generative AI for producing code.
Nestle, one of the world’s largest food and beverage companies, has been exploring using generative AI tools like OpenAI’s GPT-3 to produce code that can help automate various aspects of its operations.
By employing these advanced machine learning algorithms, Nestle aims to reduce human effort in tasks such as data analysis or customer service interactions while improving efficiency and accuracy.
Deloitte employs Codex for translating code.
Deloitte, a leading global professional services firm, is also harnessing the power of generative artificial intelligence by utilizing Codex–an advanced language model developed by OpenAI–for translating programming languages. This enables Deloitte’s developers to quickly understand existing codes written in unfamiliar languages or frameworks without spending time manually converting them into more familiar ones.
CarMax utilizes generative AI technologies for used car recommendations.
CarMax is leveraging generative AI models to provide personalized used car recommendations for their customers. By analyzing a wide variety of data points such as customer preferences, budget constraints, and vehicle features – these advanced algorithms can identify patterns and suggest vehicles that closely match individual requirements.
This enhances the shopping experience and helps CarMax optimize its inventory management processes.
The use of generative AI tools in various industries is becoming more widespread, indicating the likely positive effect on businesses’ productivity and success over time. As more organizations recognize the benefits offered by these cutting-edge technologies, we can expect even greater innovation and growth within this space.
Leveraging Generative AI Tools for SEO Improvement
Content Creation
One area where businesses can employ generative AI is in the marketing industry, especially as it relates to data.
Generative AI can be helpful in report generation, trend identification, and even campaign recommendation.
However, many people have begun experimenting with generative AI in creative fields to some mixed results. For example, generative AI has been used to create:
- Blogs: Generative AI models can create high-quality blog articles on a wide variety of topics and to edit and evaluate content already on your site. While the writing requires some massaging, generative AI can be good for overcoming writer’s block and even editing your work for grammar and SEO conciseness.
- Social Media Posts: Some companies have used generative AI to engage with users, though this still has some innovation required until the experience is seamless.
- Emails: Generative AI models can generate customized subject lines and body text that increase open rates and conversions. This technology is already being employed for A/B testing by many companies.
- Landing Pages: By generating persuasive headlines and call-to-actions (CTAs), these tools help optimize landing pages for higher conversion rates while adhering to Google’s BERT algorithm requirements.
Another area where generative AI can become invaluable is in creating personalized content in seconds for new users. Using personalized content on landing pages and ads based on user data points or in chatbots can create seamless shopping experiences that result in higher dwell times, click-through rates, and conversions.
Early adopters will be able to leverage generative AI for their white label services and client offerings to improve campaign performance.
Image Creation

One of the most creative uses of generative AI will be for image and video creation. While they may come with their own small price, the ability to create relevant images, infographics, and videos of any kind will be a game changer for the industry.
Image and video creation can be used for UX purposes, logo generation, tutorials, and even interactive displays on your website.
Tools like DreamStudio and DALL-E 2 are early pioneers in this space.
Takeaways
Generative AI has the potential to transform SEO, offering up unique content and boosting website performance which can lead to better search engine rankings and more traffic. However, there are also challenges associated with using generative AI for SEO, such as ensuring ethical use of the technology and avoiding penalties from search engines.
Overall, incorporating generative AI into your SEO strategy requires careful planning and execution. By following best practices and leveraging successful use cases, businesses can reap the benefits of this innovative technology while minimizing risks.
If you’re interested in learning more about how ContentMender can help you implement generative AI in your SEO strategy today, contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions Generative AI
What is generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a type of artificial intelligence that creates new data instances by learning patterns from existing datasets. It uses advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep learning and neural networks, to generate content like text, images, or music based on the input it receives.
What is an example of generative AI?
An example of generative AI is DALL-E, developed by OpenAI. DALL-E generates unique images from textual descriptions using deep learning algorithms trained on large-scale image-text datasets. This technology can create visually appealing and contextually relevant illustrations for various applications.
What is the impact of generative AI?
The impact of generative AI spans across industries, including marketing, entertainment, healthcare, and more. It enables businesses to automate content creation tasks while maintaining quality output. Generatively created personalized content can improve user engagement and search engine rankings; however, there are ethical concerns regarding its potential misuse and the displacement of human creators.