Because everything eventually leads back to your brand’s website, technical SEO is the foundation of all online marketing campaigns.
With just one unoptimized component, you can encounter multiple technical website issues that plague your success, such as 404 errors and poor page speed.
As important as technical SEO is to search algorithms, it’s even more important to user experience. Studies show that 40% of web users will abandon a site that doesn’t load in 3 seconds or less.
Whether you’re just starting to optimize your site or you’ve been at it for a while, these 12 basics will help you solidify your SEO foundation and improve search results.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO comprises many components of website optimization with the goal of improving organic search rankings and user experience.
While we think of technical SEO as its own discipline, it blends into many practices in which an SEO campaign manager should be well-versed, including content marketing, link building, and UX.
The fundamentals of technical SEO typically fall under one of four buckets:
- Crawling and Indexation: Ensuring pages are discoverable by search engine bots for indexation and ranking. Examples: Implementing Robots.txt tags, submitting XML sitemaps, or excluding pages with nofollow tags.
- Page Speed and Mobile Rendering: Ensuring pages load quickly and render cleanly on mobile devices. Examples: Minimizing CSS and Javascript, implementing AMP for mobile, and improving server quality.
- UX: Encompassing some design elements but ultimately ensuring that pages are clean and functional. Examples: Providing clean URLs, fixing broken links, and implementing functional calls-to-action.
- Website Architecture: Organizing pages in a top-down hierarchy to communicate their importance to users and web crawlers. Examples: Optimizing internal and external links.
Virtually every aspect of on-page and off-page SEO performance requires a sound and fast-loading website to succeed. Therefore, if you suffer from poor website rankings, lagging indexation, or many other problems, we’ve provided twenty technical SEO basics to optimize your website.
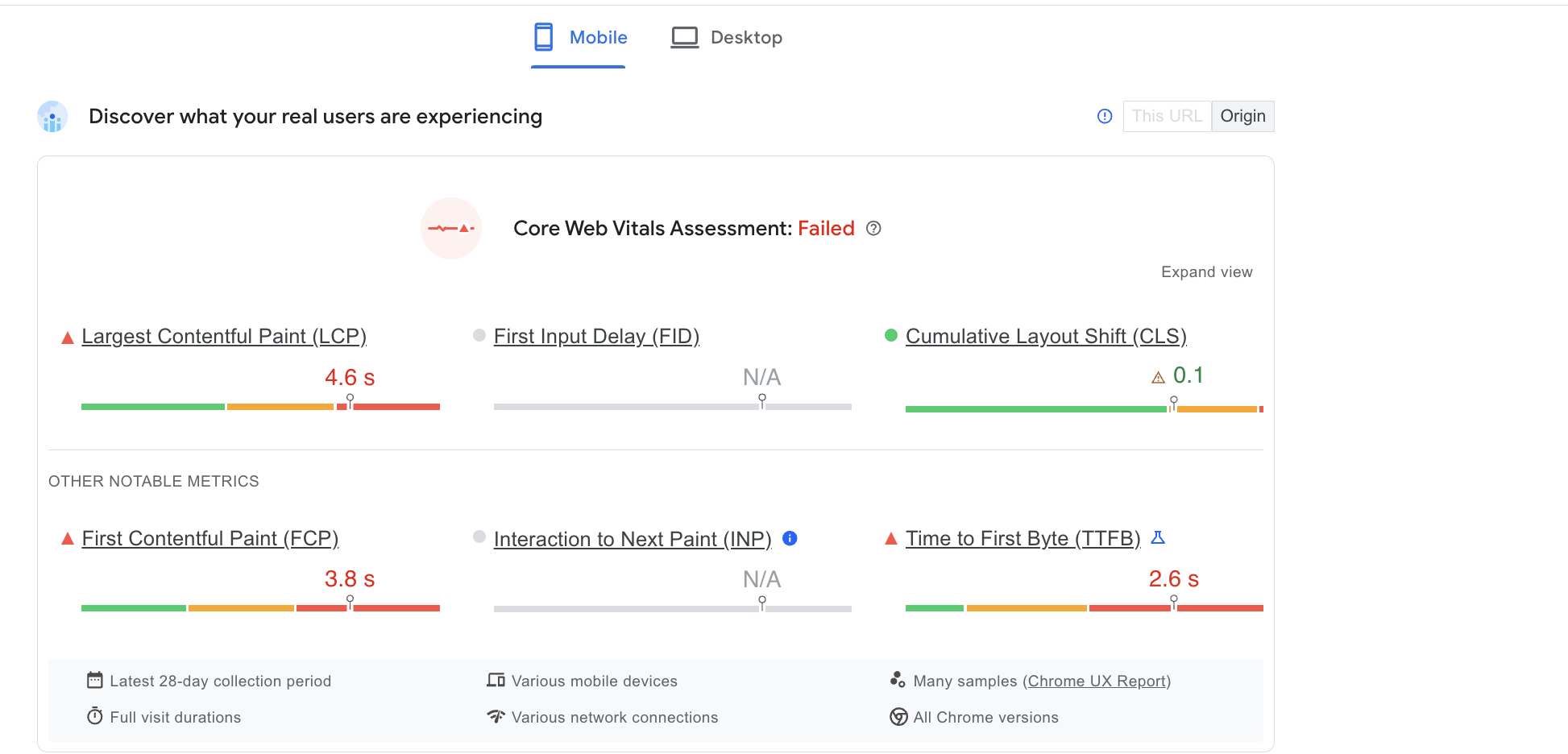
1. Improve Core Web Vitals
Page speed is an essential component of any website. Not only do slow-loading sites lead to high bounce rates, but Google has stated that page speed is a core part of its algorithm.
Google’s PageSpeed Insights goes beyond mere loading times to include important components of your UX, known as Core Web Vitals.
These three essentials are divided into:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Loading Speed. More specially, this determines how quickly different content blocks, such as images and banners, load and are viewable on your website.
- First Input Delay (FID): Interactivity. How long does it take for a user to scroll, click, or drag an object on your site?
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Stability. How much do objects on a page shift when they first load or continue to load further down a page?
Optimizing for Core Web Vitals is ultimately about optimizing for UX, as a fast and efficient site doesn’t just load quickly; it allows users to accomplish their intended tasks quickly.
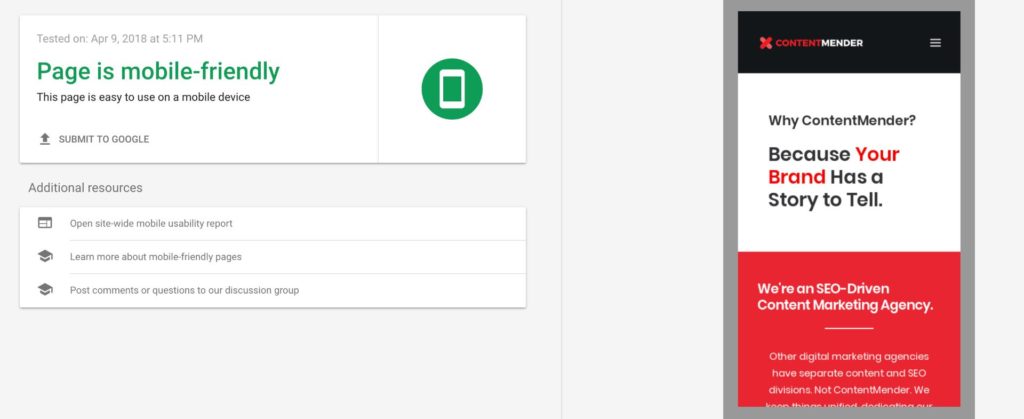
2. Prioritize Mobile
Moving beyond speed, we also have to talk about rendering. When viewing Page Speed Insights, you’ll see that a site’s performance is divided between desktop and mobile versions. This is because websites have to account for tiny screen sizes.
Optimizing websites for mobile requires an entire guide, but suffice it to say, implementing responsive web design and stripping down JavaScript and CSS requirements are essential. Other tools, such as Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), can also improve mobile page speeds.
3. Monitor Page Indexing
If Google indexes pages, organic traffic will come. If pages are not indexed, well, even the best content will be left to lead a lonely existence unseen by deserving audiences. Use Google Search Console to see how many pages are submitted and indexed. Also, you can use an SEO crawler like DeepCrawl or Screaming Frog to ensure that the content you submit to the index is indexed, obviously excluding any disallowed pages.
4. Knowing When and Where to Use Robots.txt
Improperly configured or missing robot.txt files can quickly cause a lot of damage. Robots.txt files help web-crawling software determine where it can or cannot crawl, and when implemented wrong, search engines won’t be able to crawl your site as you wish – a problem that could jeopardize other SEO efforts. Configuring your Robots.txt file is easy and you can append /robots.tx to any website to see if yours is configured properly.
5. Check for Coding Problems
If you really want to decimate your SEO efforts, have some messy source coding. If you want to avoid that scenario, then make sure seemingly small tags like NOINDEX, rel=canonical, and disallow are only used where necessary and correctly implemented. We recommend running a Screaming Frog audit (free) or any SEO or content analysis tools you own to discover any potential coding issues.
6. Keep XML SiteMaps up to Date
Your site architecture offers search engines a lay of the land and helps them identify the best “landmarks,” or pages worthy of traffic. As you can imagine, an outdated site map can be problematic, leading users and search engines to broken or irrelevant URLs. Be sure to submit an updated sitemap to Google’s Search Console if you have recently created a new site or undergone a migration.
7. Install Google Analytics and Search Console
Installing Google Analytics tracking code and Search Console is a vital aspect of any SEO campaign. Analytics tells you where users are coming from and what they are doing on your site, while Search Console will tell you what keywords are driving traffic. As a shortcut to manually installing Analytics code, we recommend setting up Google Tag Manager to upload it instead.
8. Avoid Redirect Chains
Using 301s to redirect traffic permanently can certainly be useful, but after a while, that experience can cause technical and UX issues. When auditing your site, look for an extensive chain of redirects (3 or more). If they occur, take the proper steps to address and permanently solve the problem.
9. Consider Using the Disallow Rule
Depending on your site structure, you may have many pages that are extremely important to your online presence. But most sites have a few that are just taking up space and ultimately eating into what’s considered your crawl budget, or the number of pages that a search engine will crawl at a given time.
Old promotional pages, terms and conditions, or policy pages (e.g., shipping and returns), are all pages that don’t necessarily need to be crawled, and if you find there is an issue with indexing, consider disabling them through the robots.txt mentioned in #10 above.
10. Beware of On-Page Link Saturation
Links can be a great boon to your organic presence, but a ton of links? Not so much. The only links on a page should be those that are relevant to your user’s experience and/or your SEO efforts. Avoid the “more is better mentality,” and don’t overload.
11. Use HTTPs
Security and the internet now go hand in hand, and that’s particularly true for Google. Sites without a SSL certificate will be flagged by many browsers, such as Chrome, displaying a warning signal to users.
12. Study Hreflang Tags
While more sophisticated than many other forms of technical SEO, hreflang tags are essential for any websites that serve audiences in multiple regions or languages. These HTML tags allow search engines to display copies of specific web pages that are served in different languages or abide by different laws in different countries. However, this discussion opens up a whole new can of worms that involves using region-specific subfolders, subdirectories, and domains.
The Benefits of Hiring a Consultant
Technical SEO should be an essential skill of any contractor or agency that offers basic online marketing services. Nevertheless, hiring a technical SEO consultant could often be the difference between a website that performs well and fails miserably. While many people think of it as a grudge purchase, a technical SEO consultant will guarantee that the investment you put into content will at least have the opportunity to pay off.
FAQs: Technical SEO Basics
What is the difference between technical SEO and on-page SEO?
Technical SEO: Focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of a website to improve its search engine visibility and performance. This includes factors such as website structure, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and security.
On-Page SEO: Involves optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engine results. This includes optimizing content, meta tags, headings, and internal linking. While technical SEO focuses on the infrastructure of the website, on-page SEO focuses on the content and HTML elements of individual pages.
How often should I conduct technical SEO audits for my website?
It’s recommended to conduct technical SEO audits regularly, ideally every few months or whenever there are significant changes to the website. Regular audits help identify and fix any technical issues that may impact search engine visibility and user experience. Additionally, auditing your website after major updates or changes can ensure that it remains optimized for search engines.
Can I fix technical SEO issues without coding knowledge?
Yes, many technical SEO tasks can be addressed without extensive coding knowledge. For example, optimizing website structure, improving page speed, and implementing SSL certificates can often be done through website management platforms or content management systems (CMS) like WordPress or HubSpot. However, for more complex technical issues or customization, basic coding knowledge or assistance from a web developer may be required.
Why is mobile optimization important for SEO?
Mobile optimization is crucial for SEO because of the increasing number of users accessing the internet and conducting searches on mobile devices. Google and other search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites in their search results, and mobile optimization is a ranking factor. Additionally, providing a seamless and optimized experience for mobile users improves user engagement, reduces bounce rates, and enhances overall website performance.
How can I check if my website is mobile-friendly?
There are several tools available to check if your website is mobile-friendly, including Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and tools like GTmetrix and PageSpeed Insights. These tools analyze your website’s responsiveness, mobile usability, and page speed on mobile devices. Additionally, you can manually test your website on various mobile devices and screen sizes to ensure a consistent and user-friendly experience for mobile users.