On-Page SEO Content Optimization Guide
Before we discuss how to optimize on-page SEO, remember that you must first focus on creating stellar content. Whether that’s an engaging blog that answers questions and provides endless value or a video that’s well produced.
Content continues to hold the reins of SEO strategies. As either an SEO at an agency or in-house for a business, you’ve likely devoured hundreds of articles, blogs and white papers discussing how to improve your writing and SEO practices. Unfortunately, even after all this education, you may still be clueless on how to actually start fixing your website’s content.
We’ve covered various pieces on creating engaging content. Now it’s onto a comprehensive guide for optimizing that content.
For all those who are indecisive or still-processing the unlimited amount of information online, we have a comprehensive list of top 25 best practices that can help you power up your on-page SEO to attract more qualified visitors that will turn into customers.
First…
What is On-Page SEO?
Leading SEO software company MOZ says “On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing individual web pages in order to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. On-page refers to both the content and HTML source code of a page that can be optimized, as opposed to off-page SEO which refers to links and other external signals.”
Simply put, it’s a mix and match of optimizing both the visible content and the back-end HTML code that help your website rank better on major search engines including Google.
Google, Bing, and Yahoo want to provide the best results for every search query.
Over the years, Google, for example, has rolled out hundreds of updates – Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird are the monumental ones – to better its search algorithms and improve user experience.
Many poorly-built websites have tumbled down under the weight of such updates as others strived to remove all possible glitches to stay in Google’s good books and provide the best possible results to the end-users.
Following are 25 leading factors that form an integral part of a full-fledged successful on-page SEO strategy for any type of website.
 1. SEO-friendly URLs
1. SEO-friendly URLs
Keep your URLs short and simple. Search engines crawl and index the website URL before the content. Do not stuff it with some random mumbo-jumbo to confuse the users. Instead, have a succinct URL to convey the information right away.
As Google says:
“For example, if you’re searching for information about aviation, a URL like http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aviation will help you decide whether to click that link. A URL like http://www.example.com/index.php?id_sezione=360&sid=3a5ebc944f41daa6f849f730f1, is much less appealing to users.”
Quick Tips:
- Keyword-rich URLs – use the primary keyword in the beginning if possible
- Keep it informative/relevant to your main business
- Stick with lowercase
- Avoid using underscores or spaces in their URLs. Instead, add hyphens if needed to separate words.
- Skip adding dates/years etc
- Use a robots.txt file to block Googlebot’s access to problematic URLs.
- Use HTTPS. Most visitors will immediately bounce when they see an unsecured website – even if you don’t accept payments online.
2. Page Title Tags
Title tags are undoubtedly important for your page to rank well in Google. We’d argue they are as important as the content itself.
Google bots crawl the title tags to determine the intent of the webpage. Do not mess with the basic sense of the title tags. They are the first piece of content Google bots and users will see, and that’s why it should be on your top priority.
Quick Tips:
- An informative yet engaging title
- Title length: Restrict it somewhere between 50-60 characters. Any longer will not appear on the search results page.
- Keyword-rich – use your most important keyword, especially in front of the title
- Try to add primary or second keywords, if possible. Do not stuff keywords just for SEO
- Add in the <head> section.

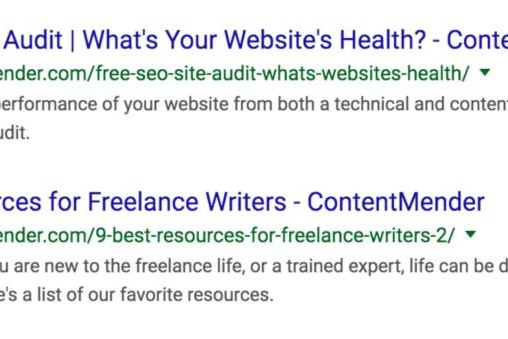
Example of a recent ContentMender title tag and meta description.
3. Meta Descriptions
These short and smart snippet of information explain what users can expect from the web page. Google says meta descriptions do not directly affect search engine ranking. But they are crucial to convey useful information to attract the users to click and visit the web page, thus boosting click-through-rates.
Read our blog about creating optimal meta descriptions.
Quick Tips:
- Descriptive yet compelling information
- Length should not exceed 160 characters (we shoot for 150-160).
- Keyword-rich: Add primary or secondary keywords to make it SEO friendly. Again, these don’t help rankings in Google but become bold when the search term is entered. This helps attract attention.
- Do not use double quotes
4. Main Header Title Tags – H1
This is the first and foremost header title (or tag) on the page. Yes – this can get confusing considering on WordPress websites, the main title tag is actually the H1
First, let’s understand the context of using header tags on your web page.
Typically, every content piece should be divided into one main heading (H1) and subsequent subheadings (H2, H3, H4, etc.). This defines the content hierarchy that organizes your entire content and makes it more readable for users.
The latter is exactly why this organization is needed – it improves the user experience, which is a major part of SEO today.
Here, we’re talking about the most important title on any page – the H1. In HTML, this looks like <h1> and goes within the <body> section. Again – WordPress calls the title of an article a H1 tag, but others have seperate title tags vs the first headline tag.
Quick Tips:
- Informative and relevant enough to know what the page is all about
- H1 Length: limit anywhere between 50-60 characters.
- Keyword-rich – using the focus keyword is mandatory
- Add primary or secondary keywords if possible
- Try to use only one H1 tag for every page
5. H2 and H3 tags
Having a single H1 tag is just the beginning, add H2 and H3 heading tags to broadly define the content for the Google bots and readers to understand. Also, this gives logical boundaries to the content so that it’s effortlessly scannable.
Quick Tips:
- Keep them relevant and in-context of the H1 tag and intent of the page
- Keyword-rich – using primary or secondary keywords
- Use keyword variations of the target keyword if possible to strengthen your on-page SEO factor.
6. Main Content
The main content is the focal point or the foundation of your entire web page. Your on-page content must reflect upon the purpose and should be descriptive enough to explain the relevant concepts for users.
Remember, Google puts user experience over and above everything else. Google bots will be tracking user behavior on the webpage whether it’s a 50-word snippet, 500-word explanation or 5,000 words full-fledged content.
For many, quick and useful information is the best. For instance, eCommerce website SEO has its own cardinal rules that often defy the standard notions.
From an SEO perspective, the longer the better. Studies suggest that the average Google first page result contains 1,890 words.
However, that’s not encrypted on the tombstone. You can take it easy and go with your common sensibilities to decide on the ideal length of the content.
If optimized well for the relevant keywords including the variations, and quality is top-class, it gives the impression of well-researched and documented content for Google to rank well for users.
Quick Tips
- High-quality well-researched informative content
- Avoid duplicate content
- Focus on the user intent to shape the content right
- Encourage organic user experience; do not stuff keywords
7. Grammatically Correct, Quality Content
Google has been pretty steady promoting relevant high-quality content as a critical factor to rank websites.
Google says for a high page quality rating, the content must display “Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness,” or what the search giant simply refers to as E-A-T.
This stands most true for companies operating in the medical and financial industry.
Try to build a reputation with your audience through content that’s authentic and stands the test of quality standards. Having silly grammatical errors are not just off-putting but puts a question mark on your sincerity towards your work.
Two of ContentMender’s favorites for grammar books are The Only Grammar Book You’ll Ever Need by Susan Thurman, and The best punction book, period. by June Casagrande.
8. Content Style/Layout
High-quality content is vital for top rankings, but small stylistic attributes can also turn off a visitor in no time. Do not forget that people are constantly bombarded with information in some form across various devices.
Pay attention to your style – from font type and sizes to shorter paragraphs to bullet points. And remain consistent across your website.
An Abode study indicates that long prose with poor layout and imagery can compel 38% of visitors to stop engaging while another 35 % will shift to other devices.
Following is an image capture from a previous blog that incorporates short paragraphs and bullet points – a style that all of ContentMender’s uploads follow:
 Quick Tips
Quick Tips
- Use legible fonts and not some fancy version
- Ensure the fonts are not too large or small
- Use short paragraphs and add bullet-points where needed
- Use bold, italics text to make it effective
9. User Intent
User behavior has undergone a dramatic transformation across various digital devices. This has reflected the need for determining the user intent that can be categorized in four ways:
- Informational
- Navigational
- Commercial
- Transactional
This helps you determine what kind of results users are looking for.
Easier said than done. Let’s take an example. If a user types SEO can you guess what exactly the user is searching for? – SEO services, SEO experts, SEO guide or just definition. There are many permutations and combinations you have to explore to determine the direction your content will take.
In such a case, Google will tumble down a variety of results based on possible user intent.
You have to polish your keyword mapping skills to find out what exactly your users expect for a specific query.
Optimizing your pages for user intent can put you closer to your audience and increase the chances of getting organic traffic for the web page.
10. Employ Related Keywords, or the Jargon-Forward “Latent Semantic Indexing”
The sole purpose behind SEO is optimizing the page for a bunch of relevant keywords to rank in Google and be accessible to the end-users. However, that does not mean you’re should flood the same keywords throughout.
Use near variations that fit in the user search intent and serve for SEO rules. To put some jargon on it, SEOs call this latent semantic indexing keywords (LSIs). They are basically variations of your main keywords.
They add thematic relevance to the on-page content.
Whether or to what extent does it help your on-page SEO content is still debatable, but using smart variations of your targeted keywords is in no way a poor deal.
11. Avoid Keyword Cannibalization
Beware of keyword cannibalization or topic duplication.
Make sure you do not falter at optimizing two or more pages for the same set of keywords or topics that can only drain your organic traffic. For instance, if you have a low-quality webpage pitted against performing target page, chances are good the former ends up drawing organic traffic but with zilch conversion rate.
This is much easier for product and e-commerce websites vs news-forward websites where multiple stories may be created about the same topic. The key is to constantly watch your search rankings, and optimize the one you want converting for that keyword phrase.
Quick Tips
- Restructure your website
- Find and flush out the offending keywords
- Use internal linking for directing visitors to the high-quality pages
- Use 301 redirects and canonical tags
- Remove poor quality pages
12. Optimize Images
You’ve got content in check but do not undermine the value of optimizing images for the relevant keywords via Alt tags and descriptions.
They define the purpose or relevance of the image and helps the crawlers index it for relevant search results for user queries.
This video of Matt Cutts is old, but explains everything clearly:
Quick Tips
- Relevant and high-quality images only
- Consider putting the image near the top of the page.
- Add the main keywords in the alt tags and accompanying description to soar up chances to rank better
13. Optimize Videos
It’s excellent for you to have videos on your website to draw more organic traffic to your website. Do not skip on its optimization the way it’s for images.
Google crawls videos using the tags such as <video>, <embed>, or <object>. Videos have high-interaction power. Resolve any crawling errors if existing. Watch the video below to know more on common video indexing pitfalls.
Quick Tips
- Short and relevant video title optimized for the main keyword
- An optimized description explaining the video
- Engaging thumbnail
- Add subtitles for those who can’t understand the language or prefer reading
- Make sure it’s not blocked by txt or noindex
- Consider adding structured data, a video sitemap, or both, describing your video
- Avoid any prolonged or complex video loading conditions
- Add videos only if relevant and supports content
14. Internal Linking
Internal links create a web form of structure with different pages connected to each other. They enable every page to be connected with a few other relevant pages within the same website.
And like many other things for strong on-page SEO, internal linking does not happen in isolation and has a calculated strategy.
Having links from authoritative sites solidifies your link building strategy but internal linking is about sharing the link equity or the link juice amongst the fellow web pages. It helps to direct users to navigate the website for a longer period of time and improves chances for lead conversion.
Quick Tips
- Every web page should be logically connected to other related categories and subcategories
- Do not overdo – limit it to 2-3 useful links for every page
- Check for broken links
- Update the links if you move the pages
15. Outbound Links
While internal links share the link authority within the website, outbound links direct crawlers and visitors to external sites. This process resembles seeking a vote of confidence or endorsement when a web page is linked to a third party site.
Do remember, not every external link adds value to your SEO strategies. Having said that it does build a reputation and adds to your credibility if you refer to a high-authority site, especially if it’s a do-follow link.
Typically, there are two types of external links:
- No Follow – prohibits Google bots to follow the links
- Do Follow – allows Google bots to follow the links and shares the authority with the targeted pages
Quick Tips
- Adopt natural and not forced outbound linking practices
- Keep the number of no follow links low
- Ensure the authority or reputation of the pages is high
- Do not overdo internal or external links. Provide them in a natural flow where readers would seek additional information
- Check for broken links. If any, fix them
- Do not use backlink network
16. Schema Markup (or Structured Data)
Schema markup has a resounding effect on your SEO practices.
In the technical parlance, schema represents a group of microdata that’s added in the HTML code for search engines to read and rank your page better.
Basically, it’s a code that enables search engines to pick relevant information from your webpage to return rich information to the end-users.
These enriched results include
- Rich search results
- Knowledge graphs
- Breadcrumbs
- Carousels
If you happen to search for roasted spaghetti squash, the result can be something like this:
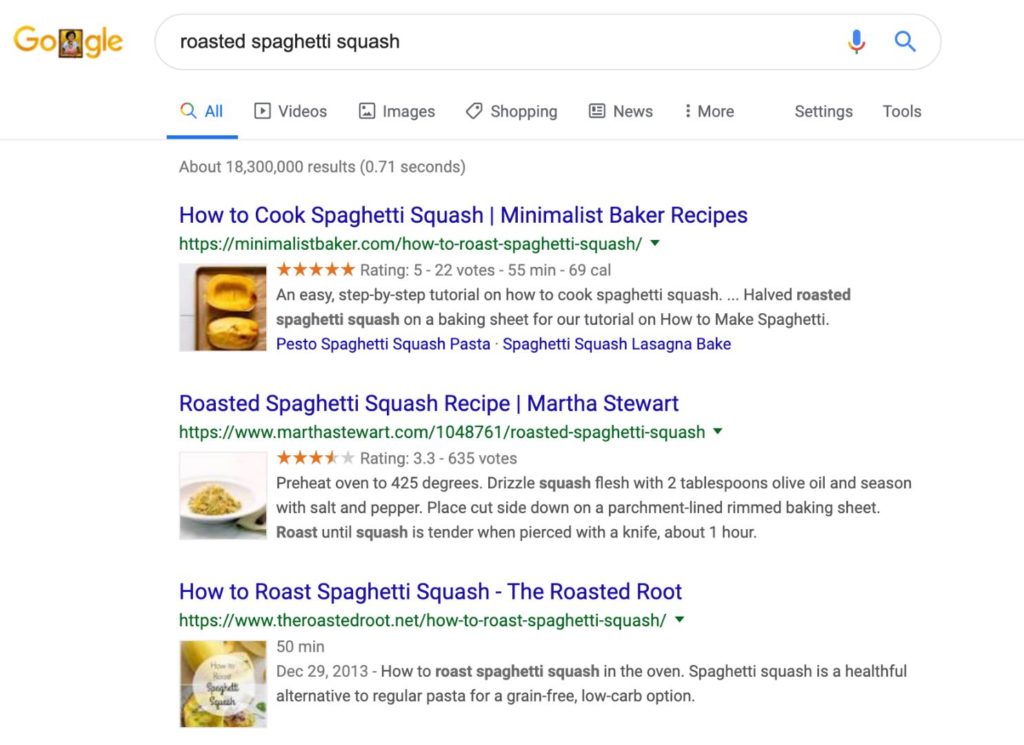
Add similar information in the HTML code to grab prominent space on the SERP and get more clicks to boost website visits and conversion. Plugins make this task easy nowadays.
17. Page Speed
There is absolutely no replacement for this on-page SEO factor. A slow website douses the flame of anticipation or excitement lasting a fraction of seconds. A faster website provides quick access to the users and does wonders for businesses.
Google has been riding high on pushing web page speed on desktops since 2010 to improve user experience. And its intention got pretty cleared when it rolled out an update on July 2018 which officially anointed Page Speed as an official factor to rank a website on mobile.
Research under the guidance of Akamai states that a mere delay of 2 seconds in the loading page shot up the bounce rate by over 100%. Such poor user experience on your website can genuinely be lethal and leaves your brand reputation in pits.
Quick Tips
- Reduce redirects
- Improve server response time
- Optimize images, videos, etc
- Remove redundant characters from the source codes of interpreted programming languages or markup languages without changing their functionality
- Enable browser caching
- Decrease the number of plugins
18. Mobile-First Indexing
Have a horrible mobile experience is no longer an option for companies.
As per Google webmasters, “Mobile-first indexing is enabled by default for all new, previously unknown to Google Search, websites starting July 1, 2019. For older sites, we’ll continue to monitor and evaluate pages for readiness, and will notify site owners through Search Console once they’re ready”.
If you haven’t done it so far, optimize your website for smartphones, notebooks, and other digital devices. Plug your URL into Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test now.
19. Add Social Media Sharing Buttons
Social media is not aloof to digital marketing practices anymore. In fact, social sharing buttons are quite prominently spotted on web pages to notch up the user experience, helping to strengthen your on-page SEO.
Adding social sharing buttons such as Facebook, Twitter, Linked In, etc on web pages enables users to share the content on their profiles to create more buzz. It generates more online visibility for your on-page content and draws clicks pushing the CTR for your website.
Going by research from BrightEdge, prominently positioned social sharing buttons boosts social sharing by a massive 700%.
Quick Tips
- Judiciously position them
- Use only relevant social sharing buttons
- Do not clutter the page
- Be selective with shareable pages
20. Add FAQs – Smart Alternatives to Featured Snippets
Features snippets are eating up a decent proportion of organic traffic. These are short, simple and direct to the point, all occurring on the top of the search results pages (position “zero”) without the need to scroll down the page.
From a short paragraph, images, lists, tables, graphs to even videos, they are aptly placed at the top of the page to grab the attention. It makes perfect sense to emulate the style through the FAQ section.
Search for a list of potential questions in relation to your main keywords. Turn to Google and narrow down your search to the “related searches” section to zero in on a handful of topics.
Answer some commonly asked questions to rank as featured snippets to win the extra clicks that do the trick.
21. Fresh Blog Content
While you’re optimizing the website for SEO, do not ignore your blog section. Blogging is a highly recommended SEO practice to entice and engage users – something for which your product or service pages have to fight for.
According to Hubspot, companies that are running a blog section on their website are likely to pocket a whopping 97% more inbound links.
Write unique and engaging blog posts on a regular basis – at least two blogs per week to get rolling!- to pique and maintain the interest of your ardent followers and draw them in for some real business.
Quick Tips
- Target long-tail keywords
- Empowers your internal linking strategy
- Draw high authority sites for outbound links
- User engagement
- Avoid using no-follow tag
22. Sitemap
Every website must have a sitemap. It enables search engines to get an insight into the hierarchy of the website i.e. web pages and their relevant position. The bots follow the XML sitemap to crawl and index the listed URLs unless you have added a “no-follow” tag.
Though submitted sitemap does not guarantee if your pages will be indexed, it does notch up the chances. Yet sitemaps have limitations of indexing a maximum of 50,000 URLs. Beyond this, you may have to add indexes for separate sitemaps such as:
- Sitemap-index-articles.xml
- sitemap-index-products.xml
- Sitemap-index-categories.xml
Quick Tips
- Use a sitemap index file if pages are large in number
- Compress sitemap files using gzip
- Only add SEO targeted pages
- Use sitemaps for different content such as image, video and Google News
- Do not add same URLs in multiple sitemaps
- Add sitemap index URLs in robots.txt and many more
23. Fix Crawling Errors
You’ve written exceptional content but what if it’s not even crawled? Populate Crawl Report from Google Search Console to determine if something is stopping the bots from accessing your website.
Check for some of the commonly found crawling errors:
- DNS Errors for broken or poor connection
- URL errors are specific to certain web pages only (410 pages, 310 redirect, etc.)
- txt file failure in situations if important pages have been disallowed
- Duplicate Content: common is eCommerce sites. Use SEMrush or Screaming Frog to determine such errors and fix them pronto before Google slaps a penalty.
- Dead or Broken links can be lethal for your website. Includes 404 error page, invalid hostname, invalid http, etc.
The biggest take away is to find and fix any crawling error that is stopping Google bots or crawlers to read your pages.
24. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text you see on a hyperlink. This enables Google bots and users to know what to expect from the content of the destination page. Be cautious while selecting the anchor text on your website which includes keyword variation, brand name, images, naked link or generic.
Although we can’t ascertain how our targeted pages are seen, Google states: “make sure that anchor text you use within your own site is useful, descriptive, and relevant.”
Quick Tips
- Short and easy-to-understand
- Relevant to the linked-to page
- Limit the use of a linked-to page only 1-2 times
- Avoid using generic unless it’s the last resort
25. Boost Dwelling time
Dwelling time is a key on-page SEO metric that defines the span of time a visitor spends on a web page before clicking on another result on the SERP. The more visitors spend time on your website, the more are the chances of lead conversion.
Remember, only search engines can configure the dwelling time correctly. All you have to do is make your web page engaging enough to serve the purpose of the visitors. Follow all the best SEO practices discussed here to entice and engage your visitors for a longer time.
However, that does not guarantee any success either. People can be unpredictable and they may still choose to look for more than just one result.
 Concluding Thoughts
Concluding Thoughts
SEO has changed over the years but there are some cardinal rules that continue to guide companies to better their website for best user experience. We have exposed 25 on-page SEO practices that remain fundamental to improve your website performance against the benchmarks search engines have set.
Share your thoughts on the top 25 best practices for on-page SEO content in the comment section below.